A available sleep support has been proven to have a shocking facet impact on mind well being, seemingly defending the organ from the buildup of the tau protein – a key biomarker within the improvement of neurodegenerative ailments together with Alzheimer’s.
The findings come out of a brand new collaboration between scientists at Washington College College of Medication in St. Louis (WashU Medication) and Japanese drug firm Eisai, which established a analysis division in 2022 to search out novel Alzheimer’s illness preventions and coverings. It is also a rising development in analysis and improvement, as scientists look to current medicines which will have makes use of past their permitted goal.
On this research, the main focus was on the sleep support lemborexant, higher recognized by its model identify Dayvigo. In contrast to a sedative, lemborexant is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant that blocks the operate of orexin, a neurotransmitter that regulates and promotes wakefulness. It is a pretty new anti-insomnia therapy, having gained approval in December 2019. Orexin receptor antagonists are additionally exhibiting promise as novel treatments for depression.
“We now have recognized for a very long time that sleep loss is a threat issue for Alzheimer’s illness,” stated senior creator David M. Holtzman, MD, Professor of Neurology at WashU Medication. “On this new research, we have now proven that lemborexant improves sleep and reduces irregular tau, which seems to be a important driver of the neurological harm that we see in Alzheimer’s and a number of other associated problems. We’re hopeful this discovering will result in additional research of this sleep medicine and the event of latest therapeutics which may be more practical than present choices both alone or together with different accessible therapies.”
Of their research, mice that had been genetically engineered to be predisposed to tau buildup had been both given lemborexant or one other sleep support, zolpidem – higher generally known as Ambien – which is in a distinct class of insomnia therapy medicine. Zolpidem as a substitute interacts with the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter, which lemborexant does not impression.
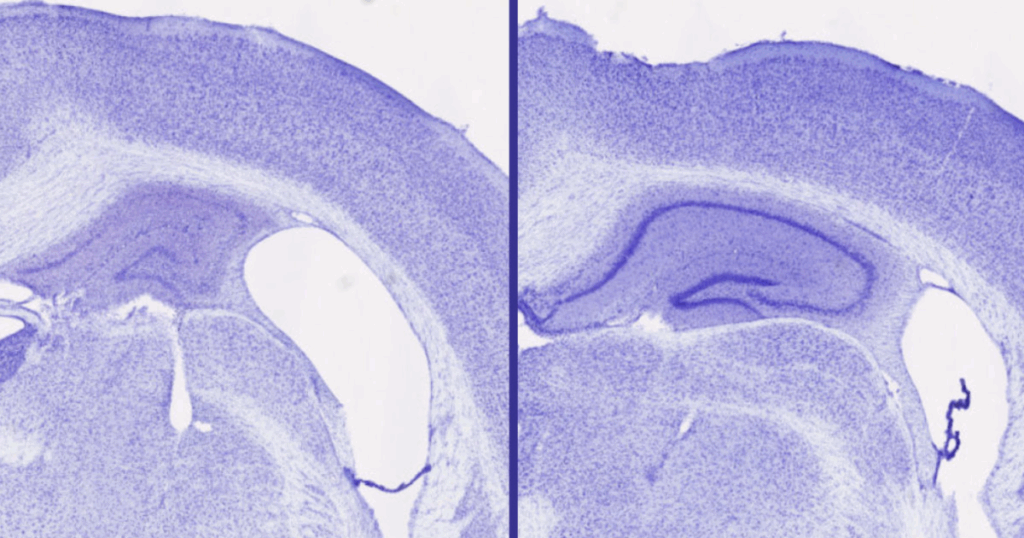
The mice on lemborexant had 30% to 40% extra mind quantity within the hippocampus – a vital space for wholesome cognitive operate – than the animals on zolpidem, though each maintained across the similar quantity of sleep. Lack of mind quantity is, in fact, a telltale signal of neurodegeneration.
Whereas Holtzman and his colleagues had been among the many first scientists to determine lack of sleep as a driver of tau and amyloid buildup within the mind, the crew discovered that it seems extra advanced than that – and that orexin receptor antagonists, in blocking dangerous protein deposits, look to have neuroprotective properties.
Nevertheless, this protecting facet impact was solely seen within the brains of male mice, which is one thing the scientists should now examine, what function intercourse performs within the course of. The crew has hypothesized that this can be on account of what we already find out about feminine mice being predisposed to tau buildup and the way it appears to trigger much less mind harm. If that is so, then the drug advantages can be tougher to detect.
Whereas the research is one other that reveals ends in the brains of mice, not people, orexin receptor antagonists might have an added benefit over different sleep aids for individuals with neurodegeneration, as they do not impair motor operate and coordination. Early outcomes present there’s promise right here to make use of a drug like lemborexant as a part of a multifaceted therapy plan.
“The antibodies to amyloid that we now use to deal with sufferers with early, delicate Alzheimer’s dementia are useful, however they don’t gradual the illness down as a lot as we wish,” he added. “We’d like methods to cut back the irregular tau buildup and its accompanying irritation, and one of these sleep support is value additional. We’re serious about whether or not going after each amyloid and tau with a mixture of therapies might be more practical at slowing or stopping the development of this illness.”
The research is printed within the journal Nature Neuroscience.
Supply: Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis