All three of the ChoiceJacking methods defeat the unique Android juice-jacking mitigations. Certainly one of them additionally works towards these defenses in Apple units. In all three, the charger acts as a USB host to set off the affirmation immediate on the focused cellphone.
The assaults then exploit numerous weaknesses within the OS that enable the charger to autonomously inject “enter occasions” that may enter textual content or click on buttons introduced in display screen prompts as if the consumer had carried out so immediately into the cellphone. In all three, the charger ultimately good points two conceptual channels to the cellphone: (1) an enter one permitting it to spoof consumer consent and (2) a file entry connection that may steal recordsdata.
An illustration of ChoiceJacking assaults. (1) The sufferer gadget is hooked up to the malicious charger. (2) The charger establishes an additional enter channel. (3) The charger initiates a knowledge connection. Person consent is required to verify it. (4) The charger makes use of the enter channel to spoof consumer consent.
Credit score:
Draschbacher et al.
It’s a keyboard, it’s a number, it’s each
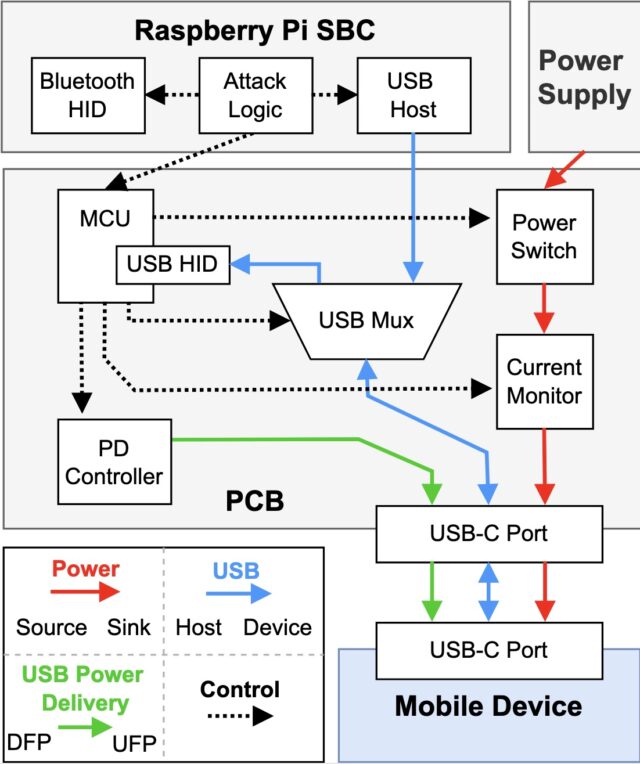
Within the ChoiceJacking variant that defeats each Apple- and Google-devised juice-jacking mitigations, the charger begins as a USB keyboard or the same peripheral gadget. It sends keyboard enter over USB that invokes easy key presses, corresponding to arrow up or down, but additionally extra complicated key combos that set off settings or open a standing bar.
The enter establishes a Bluetooth connection to a second miniaturized keyboard hidden contained in the malicious charger. The charger then makes use of the USB Power Delivery, an ordinary accessible in USB-C connectors that enables units to both present or obtain energy to or from the opposite gadget, relying on messages they alternate, a course of referred to as the USB PD Knowledge Function Swap.
A simulated ChoiceJacking charger. Bidirectional USB traces enable for knowledge position swaps.
Credit score:
Draschbacher et al.
With the charger now appearing as a number, it triggers the file entry consent dialog. On the identical time, the charger nonetheless maintains its position as a peripheral gadget that acts as a Bluetooth keyboard that approves the file entry consent dialog.
The complete steps for the assault, offered within the Usenix paper, are:
1. The sufferer gadget is related to the malicious charger. The gadget has its display screen unlocked.
2. At an appropriate second, the charger performs a USB PD Knowledge Function (DR) Swap. The cellular gadget now acts as a USB host, the charger acts as a USB enter gadget.
3. The charger generates enter to make sure that BT is enabled.
4. The charger navigates to the BT pairing display screen within the system settings to make the cellular gadget discoverable.
5. The charger begins promoting as a BT enter gadget.
6. By always scanning for newly discoverable Bluetooth units, the charger identifies the BT gadget handle of the cellular gadget and initiates pairing.
7. Via the USB enter gadget, the charger accepts the Sure/No pairing dialog showing on the cellular gadget. The Bluetooth enter gadget is now related.
8. The charger sends one other USB PD DR Swap. It’s now the USB host, and the cellular gadget is the USB gadget.
9. Because the USB host, the charger initiates a knowledge connection.
10. Via the Bluetooth enter gadget, the charger confirms its personal knowledge connection on the cellular gadget.
This system works towards all however one of many 11 cellphone fashions examined, with the holdout being an Android gadget working the Vivo Funtouch OS, which doesn’t totally help the USB PD protocol. The assaults towards the ten remaining fashions take about 25 to 30 seconds to determine the Bluetooth pairing, relying on the cellphone mannequin being hacked. The attacker then has learn and write entry to recordsdata saved on the gadget for so long as it stays related to the charger.


