Massive Language fashions (LLMs) have witnessed spectacular progress and these giant fashions can do quite a lot of duties, from producing human-like textual content to answering questions. Nonetheless, understanding how these fashions work nonetheless stays difficult, particularly due a phenomenon referred to as superposition the place options are blended into one neuron, making it very troublesome to extract human comprehensible illustration from the unique mannequin construction. That is the place strategies like sparse Autoencoder seem to disentangle the options for interpretability.
On this weblog submit, we are going to use the Sparse Autoencoder to search out some function circuits on a specific attention-grabbing case of subject-verb settlement ,and perceive how the mannequin parts contribute to the duty.
Key ideas
Function circuits
Within the context of neural networks, function circuits are how networks study to mix enter options to type advanced patterns at increased ranges. We use the metaphor of “circuits” to explain how options are processed alongside layers in a neural community as a result of such processes remind us of circuits in electronics processing and mixing indicators.
These function circuits type steadily by means of the connections between neurons and layers, the place every neuron or layer is chargeable for reworking enter options, and their interactions result in helpful function combos that play collectively to make the ultimate predictions.
Right here is one instance of function circuits: in a lot of imaginative and prescient neural networks, we will discover “a circuit as a household of models detecting curves in numerous angular orientations. Curve detectors are primarily carried out from earlier, much less subtle curve detectors and line detectors. These curve detectors are used within the subsequent layer to create 3D geometry and complicated form detectors” [1].
Within the coming chapter, we are going to work on one function circuit in LLMs for a subject-verb settlement process.
Superposition and Sparse AutoEncoder
Within the context of Machine Learning, we’ve got generally noticed superposition, referring to the phenomenon that one neuron in a mannequin represents a number of overlapping options quite than a single, distinct one. For instance, InceptionV1 accommodates one neuron that responds to cat faces, fronts of vehicles, and cat legs.
That is the place the Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) is available in.
The SAE helps us disentangle the community’s activations right into a set of sparse options. These sparse options are usually human comprehensible,m permitting us to get a greater understanding of the mannequin. By making use of an SAE to the hidden layers activations of an LLM mode, we will isolate the options that contribute to the mannequin’s output.
You’ll find the main points of how the SAE works in my former blog post.
Case examine: Topic-Verb Settlement
Topic-Verb Settlement
Topic-verb settlement is a elementary grammar rule in English. The topic and the verb in a sentence have to be constant in numbers, aka singular or plural. For instance:
- “The cat runs.” (Singular topic, singular verb)
- “The cats run.” (Plural topic, plural verb)
Understanding this rule easy for people is vital for duties like textual content technology, translation, and query answering. However how do we all know if an LLM has really discovered this rule?
We’ll now discover on this chapter how the LLM kinds a function circuit for such a process.
Constructing the Function Circuit
Let’s now construct the method of making the function circuit. We’d do it in 4 steps:
- We begin by inputting sentences into the mannequin. For this case examine, we think about sentences like:
- “The cat runs.” (singular topic)
- “The cats run.” (plural topic)
- We run the mannequin on these sentences to get hidden activations. These activations stand for the way the mannequin processes the sentences at every layer.
- We go the activations to an SAE to “decompress” the options.
- We assemble a function circuit as a computational graph:
- The enter nodes characterize the singular and plural sentences.
- The hidden nodes characterize the mannequin layers to course of the enter.
- The sparse nodes characterize obtained options from the SAE.
- The output node represents the ultimate resolution. On this case: runs or run.
Toy Mannequin
We begin by constructing a toy language mannequin which could haven’t any sense in any respect with the next code. It is a community with two easy layers.
For the subject-verb settlement, the mannequin is meant to:
- Enter a sentence with both singular or plural verbs.
- The hidden layer transforms such info into an summary illustration.
- The mannequin selects the right verb type as output.
# ====== Outline Base Mannequin (Simulating Topic-Verb Settlement) ======
class SubjectVerbAgreementNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
tremendous().__init__()
self.hidden = nn.Linear(2, 4) # 2 enter → 4 hidden activations
self.output = nn.Linear(4, 2) # 4 hidden → 2 output (runs/run)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def ahead(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.hidden(x)) # Compute hidden activations
return self.output(x) # Predict verbIt’s unclear what occurs contained in the hidden layer. So we introduce the next sparse AutoEncoder:
# ====== Outline Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) ======
class c(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim):
tremendous().__init__()
self.encoder = nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim) # Decompress to sparse options
self.decoder = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, input_dim) # Reconstruct
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def ahead(self, x):
encoded = self.relu(self.encoder(x)) # Sparse activations
decoded = self.decoder(encoded) # Reconstruct authentic activations
return encoded, decodedWe prepare the unique mannequin SubjectVerbAgreementNN and the SubjectVerbAgreementNN with sentences designed to characterize completely different singular and plural types of verbs, akin to “The cat runs”, “the infants run”. Nonetheless, similar to earlier than, for the toy mannequin, they could not have precise meanings.
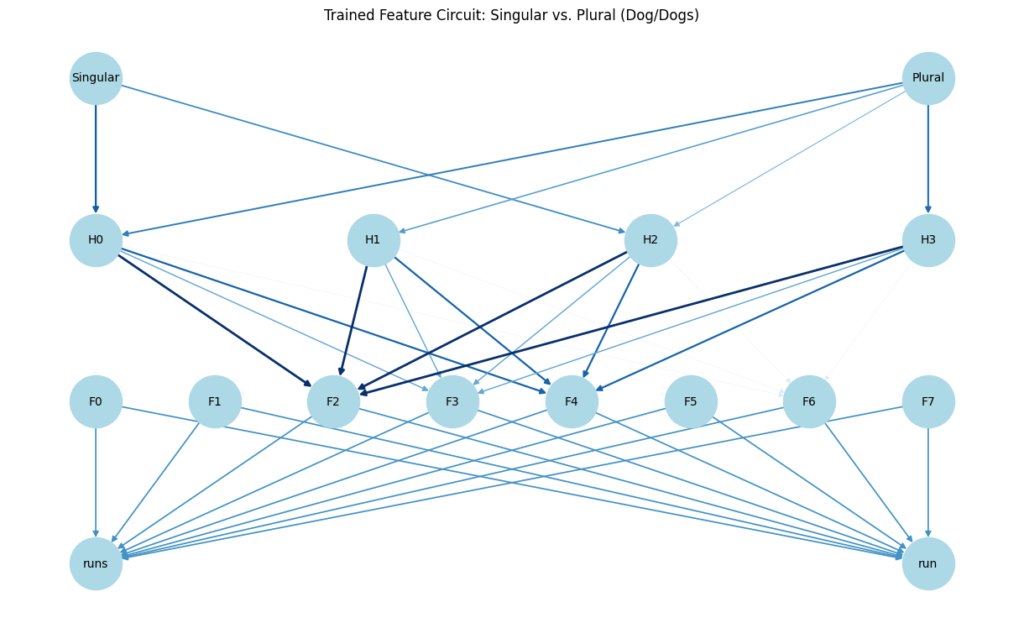
Now we visualise the function circuit. As launched earlier than, a function circuit is a unit of neurons for processing particular options. In our mannequin, the function consists:
- The hidden layer reworking language properties into summary illustration..
- The SAE with unbiased options that contribute on to the verb -subject settlement process.
You possibly can see within the plot that we visualize the function circuit as a graph:
- Hidden activations and the encoder’s outputs are all nodes of the graph.
- We even have the output nodes as the right verb.
- Edges within the graph are weighted by activation energy, displaying which pathways are most vital within the subject-verb settlement resolution. For instance, you possibly can see that the trail from H3 to F2 performs an vital position.
GPT2-Small
For an actual case, we run the same code on GPT2-small. We present the graph of a function circuit representing the choice to decide on the singular verb.

Conclusion
Function circuits assist us to grasp how completely different components in a posh LLM result in a closing output. We present the chance to make use of an SAE to type a function circuit for a subject-verb settlement process.
Nonetheless, we’ve got to confess this technique nonetheless wants some human-level intervention within the sense that we don’t at all times know if a circuit can actually type with out a correct design.
Reference
[1] Zoom In: An Introduction to Circuits
Source link