Individuals who sit on the low or excessive aspect of regular vitamin B12 ranges are nonetheless prone to cognitive impairment, in line with a brand new research. The researchers behind the research say we have to rethink the ‘wholesome’ vary for the vitamin that performs a key position in mind and nerve well being.
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is essential in DNA synthesis, purple blood cell formation, nervous system well being and performance, mind well being, and vitality manufacturing. It’s usually obtained by meat, poultry, fish and shellfish, dairy merchandise and eggs. Vegans and vegetarians can receive B12 from meals fortified with the vitamin.
A brand new research led by UC San Francisco (UCSF) researchers has examined how seemingly ‘regular’ blood ranges of vitamin B12 can nonetheless negatively have an effect on mind functioning and construction, particularly in older people.
“Earlier research that outlined well being quantities of B12 could have missed delicate practical manifestations of excessive or low ranges that may have an effect on individuals with out inflicting over signs,” stated the research’s corresponding creator, Dr Ari Inexperienced, from the College’s Weill Institute for Neuroscience and its Division of Ophthalmology. “Revisiting the definition of B12 deficiency to include practical biomarkers may result in earlier intervention and prevention of cognitive decline.”
After vitamin B12 is absorbed into the bloodstream, two service proteins assist it get to the place it’s wanted within the physique. One, haptocorrin (HC), binds to a lot of the B12 within the blood, however the physique can’t use it right away, so it primarily leads to the liver, the place it’s ultimately damaged down and excreted. This type of B12 is taken into account biologically inactive as a result of it’s not instantly obtainable to the tissues. The second protein, transcobalamin (TC), binds to a smaller portion of B12 because of a receptor referred to as CD320 that enables cells to soak up it. Ready for use by the physique instantly, this type of B12 is taken into account biologically lively.
When blood ranges of B12 are measured, each kinds are measured. The lively B12 (Holo-TC) is what actually issues for the physique’s cells. If it’s low, it could possibly trigger neurological signs. However, the inactive B12 (Holo-HC) is generally simply ‘in storage’ within the liver and doesn’t immediately assist with bodily capabilities. In america, the UK, and Australia, concentrations of vitamin B12 within the blood are measured in numerous models. To supply a constant comparability, the reference ranges for every nation have been transformed to picomoles per liter (pmol/L):
- United States: 148 to 748 pmol/L
- Australia: 135 to 650 pmol/L
- United Kingdom: 115 to 740 pmol/L
So, within the US, the place the current research was carried out, a B12 ‘deficiency’ could be outlined as a price under 148 pmol/L and ‘regular’ could be any focus that falls throughout the above reference vary.
For the current research, the researchers enrolled 231 wholesome research contributors with a median age of 71 years and a median B12 blood focus of 414.8 pmol/L, nicely above the advisable decrease stage. Individuals have been recruited by the Brain Aging Network for Cognitive Health (BrANCH) research at UCSF. The researchers measured contributors’ complete blood B12 and Holo-TC ranges. Holo-HC values have been inferred by subtracting Holo-TC from the entire measured B12.
The researchers evaluated the affiliation of B12 concentrations with cognitive efficiency and myelin integrity. Myelin is the protecting coating round nerve fibers and is essential for correct nerve operate. Vitamin B12 performs a key position in sustaining it. When B12 is poor, the physique struggles to restore and preserve myelin’s integrity. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans have been taken to evaluate the well being of mind tissue.
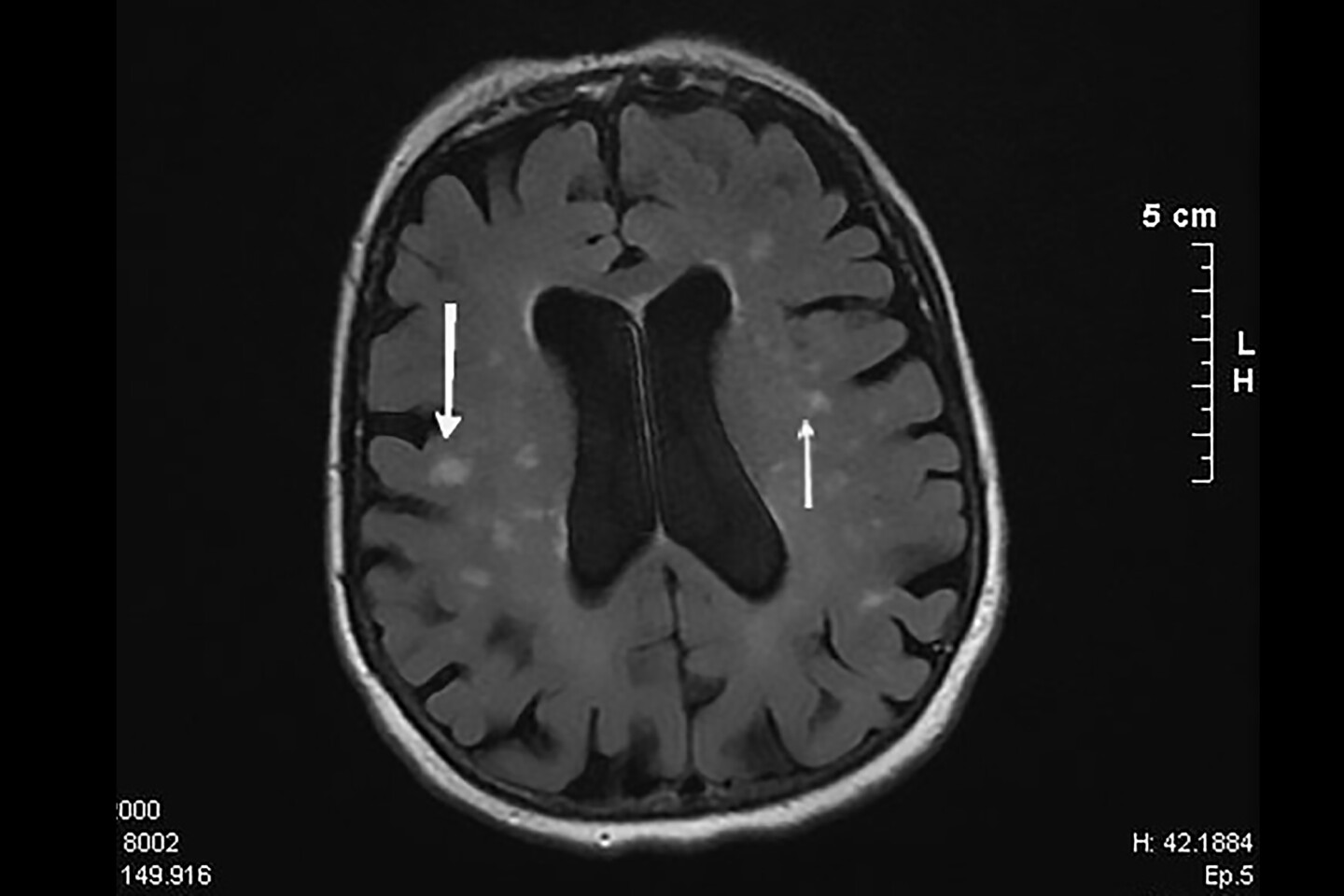
They discovered that decrease ranges of B12, particularly the lively kind (Holo-TC), have been related to slower cognitive processing speeds. The impact was worse with age, which means that older adults with low Holo-TC have been extra affected. Low Holo-TC was additionally linked to slower nerve signaling referring to imaginative and prescient. Moreover, MRI scans revealed that contributors with decrease Holo-TC had extra ‘white matter hyperintensities’ (WMH), small areas of harm within the mind’s white matter related to growing old, poor circulation, or neurological ailments like stroke or dementia. The researchers couldn’t inform from this research whether or not the WMH seen on MRI was a direct results of low B12. The researchers discovered it stunning that greater ranges of the inactive type of B12 (Holo-HC) have been linked to greater serum tau ranges, a protein related to mind cell degeneration and circumstances like Alzheimer’s illness.
The research’s findings are related to present scientific follow and will facilitate a change in therapy, particularly in older sufferers.
“Along with redefining B12 deficiency, clinicians ought to rethink supplementation in older sufferers with neurological signs even when their ranges are inside regular limits,” stated the research’s co-lead creator, Alexandra Beaudry-Richard, who’s finishing her doctorate in analysis and medication at UCSF’s Division of Neurology.
The research was revealed within the journal Annals of Neurology.
Supply: UCSF


