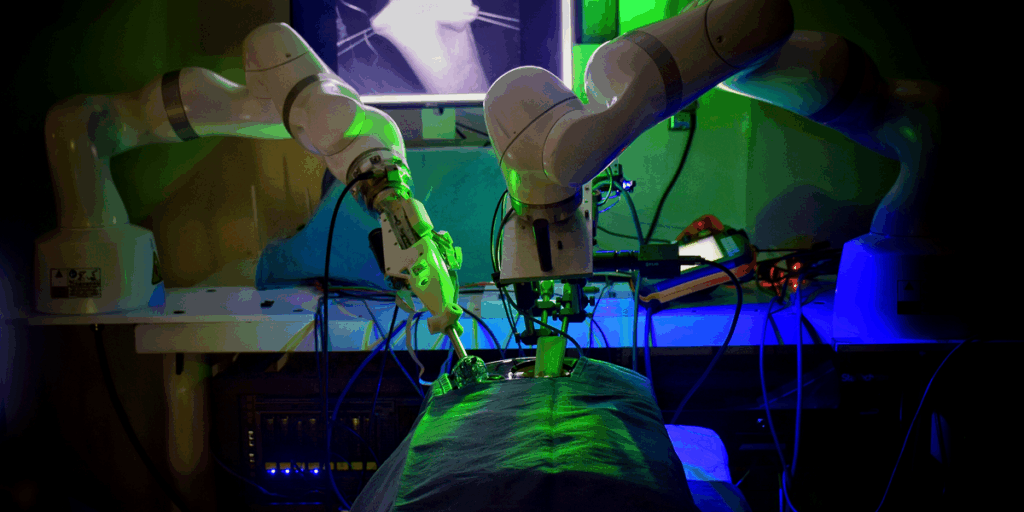
Right here’s a scene from the not-too-distant future. In a shiny, high-tech operating room, a smooth robotic arm stands poised subsequent to the working desk. The autonomous robotic received’t function fully alone, however it is going to help within the upcoming process, performing key duties independently with enhanced precision and decreased threat.
Its affected person is one in all more than 150,000 patients identified with colon cancer within the United States alone every year. The one healing remedy is to take away the diseased a part of the colon—ideally in a minimally invasive laparoscopic process, carried out with surgical tools and a skinny digital camera inserted by means of small incisions. However the surgery tends to be difficult. The surgeon’s abilities, expertise, and approach are essentially the most important factors influencing surgical outcomes and complications, which happen in as much as 16 percent of cases. These problems can diminish the affected person’s high quality of life and improve the danger of loss of life. The hope is that an autonomous surgical robotic will enhance these odds.
See the Sensible Tissue Autonomous Robotic (STAR) in motion on this video demonstrating how the system laparoscopically sutures a bit of small gut.
Throughout surgical procedure, this robotic will carry out duties that require the utmost accuracy. The surgeon will first management its motions by hand to take away the cancerous tissue, then supervise the robotic’s movement because it independently sews the remaining wholesome colon again collectively. Utilizing a number of types of imaging and real-time surgical planning, the robotic will place every sew with submillimeter precision, a feat not potential with human palms. Consequently, the ensuing suture line shall be stronger and extra uniform, making it much less prone to leak, a harmful complication that may happen when the connection doesn’t heal correctly.
Whereas autonomous robots aren’t but getting used to function on folks in the way in which we’ve simply described, we now have the instruments able to this futuristic type of surgical procedure, with extra autonomy on the way in which. Our group, centered round coauthor Axel Krieger’s robotics lab at Johns Hopkins University, in Baltimore, is devoted to growing robots that may carry out advanced, repetitive duties extra persistently and precisely than the best surgeons. Earlier than too lengthy, a affected person might anticipate to listen to a brand new model of the acquainted greeting: “The robotic will see you now.”
Robotic-assisted surgical procedure dates back to 1985, when a group of surgeons at Lengthy Seashore Memorial Medical Heart, Calif., used an tailored industrial robot arm to information a needle right into a mind for a biopsy. Though the process went properly, Westinghouse, the robotic’s producer, halted additional surgical procedures. The corporate argued that as a result of the robotic was designed for industrial purposes, it lacked crucial security options. Regardless of this hitch, surgical robots continued to evolve. In 1994, U.S. regulators accredited the primary surgical robotic: the Automated Endoscopic System for Optimum Positioning (AESOP), a voice-controlled robotic arm for laparoscopic digital camera positioning. The 12 months 2000 noticed the introduction of the da Vinci robot, a teleoperated system that permits surgeons to have tremendous management over tiny devices.
The primary model of STAR sutured a bit of small gut pulled up by means of an incision.Ryan Decker
Surgeons are a cautious bunch, and so had been initially gradual to undertake the know-how. In 2012, lower than 2 % of surgical procedures in america concerned robots, however by 2018, that number rose to about 15 percent. Surgeons discovered that robots supplied clear benefits for sure procedures, such because the elimination of the prostate gland—in the present day, more than 90 percent of such procedures in america are robot-assisted. However the advantages for a lot of different surgical procedures stay unsure. The robots are costly, and the human surgeons who use them require specialised coaching, main some consultants to query the general utility of robotic help in surgical procedures.
Nevertheless, autonomous robotic methods, which may deal with discrete duties on their very own, may doubtlessly display higher efficiency with much less human coaching required. Surgical procedure requires spectacular precision, regular palms, and a excessive diploma of medical experience. Studying how you can safely carry out specialised procedures takes years of rigorous coaching, and there may be little or no room for human error. With autonomous robotic methods, the excessive demand for security and consistency throughout surgical procedure may extra simply be met. These robots may handle routine duties, stop errors, and doubtlessly carry out full operations with little human enter.
The necessity for innovation is obvious: The variety of surgeons all over the world is shortly lowering, whereas the quantity of people that want surgical procedure continues to extend. A 2024 report by the Affiliation of American Medical Schools predicted a U.S. scarcity of as much as 19,900 surgeons by the 12 months 2036. These robots current a manner for hundreds of thousands of individuals to achieve entry to high-quality surgical procedure. So why aren’t autonomous surgical procedures being carried out but?
Usually, after we consider robots within the office, we think about them finishing up manufacturing unit duties, like sorting packages or assembling vehicles. Robots have excelled in such environments, with their managed situations and the comparatively small quantity of variation in duties. For instance, in an auto manufacturing unit, robots within the assembly line set up the very same components in the very same place for each automotive. However the complexity of surgical procedures—characterised by dynamic interactions with smooth tissues, blood vessels, and organs—doesn’t simply translate to robotic automation. Not like managed manufacturing unit settings, every surgical state of affairs presents surprising conditions that require making selections in actual time. That is additionally why we don’t but see robots in our day-to-day lives; the world round us is stuffed with surprises that require adapting on the fly.
Growing robots able to navigating the intricacies of the human physique is a formidable problem that requires subtle mechanical design, modern imaging methods, and most not too long ago, superior artificial-intelligence algorithms. These algorithms should be able to processing real-time information in an effort to adapt to the unpredictable setting of the human physique.
STAR: An Autonomous Surgical Bot
2016 marked a serious milestone for our subject: One in all our group’s robotic methods performed the primary autonomous soft-tissue surgical procedure in a stay animal. Referred to as the Smart Tissue Autonomous Robot, or STAR, it sewed collectively tissue within the small gut of a pig utilizing a commercially obtainable robot arm whereas supervised by a human surgeon. The robotic moved independently between suturing areas alongside the tissue edge and waited for the surgeon’s approval earlier than autonomously putting the stitches. This management technique, referred to as supervised autonomy, is usually used to verify surgeons keep engaged when automating a essential activity.
STAR’s suturing was the primary time a robotic had demonstrated autonomous surgical efficiency that was objectively higher than the usual of care: In contrast with the efficiency of human surgeons, STAR achieved extra constant suture spacing, which creates a stronger and extra sturdy suture line. And a stronger sew line can face up to greater pressures from inside the gut with out leaking, in contrast with sutures performed by the guide laparoscopic approach. We take into account this a groundbreaking achievement, as such leaks are essentially the most dreaded complication for sufferers receiving any sort of gastrointestinal surgical procedure. As much as 20 percent of sufferers receiving surgical procedure to reconnect the colon develop a leak, which may trigger life-threatening infections and will require further surgical procedure.
 The 2016 STAR system sutures the small gut with a single robotic arm. Behind the robotic, a display reveals near-infrared and 3D imaging aspect by aspect. Ryan Decker
The 2016 STAR system sutures the small gut with a single robotic arm. Behind the robotic, a display reveals near-infrared and 3D imaging aspect by aspect. Ryan Decker
Earlier than this 2016 surgical procedure, autonomous soft-tissue surgical procedure was thought of a fantasy of science fiction. As a result of smooth tissue consistently shifts and contorts, the surgical subject modifications every time the tissue is touched, and it’s inconceivable to make use of presurgical imaging to information a robotic’s movement. We had additionally been stymied by the state of surgical imaging. The most effective cameras that had been suitable with surgical scopes—the lengthy, skinny tubes used to view inner surgical procedures—lacked the quantifiable depth info that autonomous robots want for navigation.
Vital improvements in surgical instruments and imaging made the STAR robotic successful. As an illustration, the system sutured with a curved needle, simplifying the movement wanted to go a needle by means of tissue. Moreover, a brand new design allowed a single robotic arm to each information the needle and management the suture rigidity, so there was no threat of instruments colliding within the surgical subject.
However an important innovation that made STAR potential was the usage of a novel dual-camera system that enabled real-time monitoring of the gut throughout surgical procedure. The primary digital camera offered colour pictures and quantifiable three-dimensional details about the surgical subject. Utilizing this info, the system created surgical plans by imaging the intestinal tissue and figuring out the optimum areas for the stitches to yield the specified suture spacing. However on the time, the imaging charge of the system was restricted to 5 frames per second—not quick sufficient for real-time software.
To resolve this limitation, we launched a second, near-infrared digital camera that took about 20 images per second to trace the positions of near-infrared markers positioned on the goal tissue. When the place of a given marker moved an excessive amount of from one body to the following, the system would pause and replace the surgical plan based mostly on information from the slower digital camera, which produced three-dimensional pictures. This technique enabled STAR to trace the soft-tissue deformations in two-dimensional area in actual time, updating the three-dimensional surgical plan solely when tissue motion jeopardized its success.
This version of STAR may place a suture on the right location on the primary attempt a bit of greater than half the time. In observe, this meant that the STAR system wanted a human to maneuver the suture needle—after it had already pierced the pores and skin—as soon as each 2.37 stitches. That charge was almost on par with how often human surgeons need to right the needle place when manually controlling a robotic: as soon as each 2.27 stitches. The variety of stitches utilized per needle adjustment is a essential metric for quantifying how a lot collateral tissue is broken throughout a surgical procedure. Usually, the less occasions tissue is pierced throughout surgical procedure (which corresponds to a better variety of sutures per adjustment), the higher the surgical outcomes for the affected person.
For its time, the STAR system was a revolutionary achievement. Nevertheless, its dimension and restricted dexterity hindered medical doctors’ enthusiasm, and it was by no means used on a human affected person. STAR’s imaging system was a lot greater than the cameras and endoscopes utilized in laparoscopic surgical procedures, so it may carry out intestinal suturing solely by means of an open surgical approach during which the gut is pulled up by means of a pores and skin incision. To switch STAR for laparoscopic surgical procedures, we would have liked one other spherical of innovation in surgical imaging and planning.
Bettering STAR’s Surgical Autonomy
In 2020 (outcomes printed in 2022), the following technology of STAR set one other file on the earth of soft-tissue surgical procedure: the primary autonomous laparoscopic surgery in a live animal (once more, intestinal surgical procedure in a pig). The system featured a brand new endoscope that generates three-dimensional pictures of the surgical scene in actual time by illuminating tissue with patterns of sunshine and measuring how the patterns are distorted. What’s extra, the endoscope’s dimensions had been sufficiently small to permit the digital camera to suit inside the opening used for the laparoscopic process.

 The autonomy afforded by the 2020 STAR system permits surgeons to take a step again from the surgical subject [top]. Axel Krieger [bottom] takes a detailed have a look at STAR’s suturing. Max Aguilera Hellweg
The autonomy afforded by the 2020 STAR system permits surgeons to take a step again from the surgical subject [top]. Axel Krieger [bottom] takes a detailed have a look at STAR’s suturing. Max Aguilera Hellweg
Adapting STAR for a laparoscopic method affected each a part of the system. As an illustration, these procedures happen inside restricted workspace within the affected person’s stomach, so we had so as to add a second robotic arm to keep up the correct rigidity within the suturing thread—all whereas avoiding collisions with the suturing arm. To assist STAR autonomously manipulate thread and to maintain the suture from tangling with accomplished stitches, we added a second joint to the robotic’s surgical instruments, which enabled wristlike motions.
Now that the gut was to be sutured laparoscopically, the tissue needed to be held in place with short-term sutures in order that STAR’s endoscope may visualize it—a step generally performed within the nonrobotic equal of this process. However by anchoring the gut to the belly wall, the tissue would transfer with every breath of the animal. To compensate for this motion, we used machine learning to detect and measure the motions attributable to every breath, then direct the robotic to the suitable suture location. In these procedures, STAR generated choices for the surgical plan earlier than the primary sew, detected and compensated for movement inside the stomach, and accomplished most suturing motions within the surgical plan with out surgeon enter. This management technique, referred to as activity autonomy, is a elementary step towards the total surgical autonomy we envision for future methods.
Whereas the unique STAR’s methodology of tissue detection nonetheless relied on the usage of near-infrared markers, latest developments in deep learning have enabled autonomous tissue monitoring with out these markers. Machine studying methods in image processing additionally shrank the endoscope to 10 millimeters in diameter and enabled simultaneous three-dimensional imaging and tissue monitoring in actual time, whereas sustaining the identical accuracy of STAR’s earlier cameras.
All these advances enabled STAR to make tremendous changes throughout an operation, which have decreased the variety of corrective actions by the surgeon. In observe, this new STAR system can autonomously full 5.88 stitches earlier than a surgeon wants to regulate the needle place—a significantly better final result than what a surgeon can obtain when working a robotic manually for the complete process, guiding the needle by means of each sew. By comparability, when human surgeons carry out laparoscopic surgical procedure with none robotic help, they regulate their needle place after nearly each sew.
AI and machine studying strategies will possible proceed to play a distinguished function as researchers push the boundaries of what surgical jobs will be accomplished utilizing activity automation. Ultimately, these strategies may result in a extra full sort of automation that has eluded surgical robots—thus far.
The Way forward for Robotic Surgical procedure
With every technical advance, autonomous surgical robots inch nearer to the working room. However to make these robots extra usable in medical settings, we’ll must equip the machines with the instruments to see, hear, and maneuver extra like a human. Robots can use computer vision to interpret visible information, natural-language processing to grasp spoken directions, and superior motor management for exact actions. Integrating these methods will imply {that a} surgeon can verbally instruct the robotic to “grasp the tissue on the left”or “tie a knot right here,” as an illustration. In conventional robotic surgical procedure methods, against this, every motion must be described utilizing advanced mathematical equations.
 Specialised imaging permits STAR’s laparoscopic suturing. The purple dots right here present the system’s proposed suture areas. Hamed Saeidi
Specialised imaging permits STAR’s laparoscopic suturing. The purple dots right here present the system’s proposed suture areas. Hamed Saeidi
To construct such robots, we’ll want general-purpose robotic controllers able to studying from huge datasets of surgical procedures. These controllers will observe professional surgeons throughout their coaching and learn to adapt to unpredictable conditions, corresponding to soft-tissue deformation throughout surgical procedure. Not like the consoles utilized in in the present day’s robotic surgical procedures, which give human surgeons direct management, this future robotic controller willuse AI to autonomously handle the robotic’s actions and decision-making throughout surgical duties, decreasing the necessity for fixed human enter—whereas retaining the robotic below a surgeon’s supervision.
Surgical robots working on human sufferers will collect an unlimited quantity of knowledge and, ultimately, the robotic methods can prepare on that information to learn to deal with duties they weren’t explicitly taught. As a result of these robots function in managed environments and carry out repetitive duties, they will repeatedly be taught from new information, enhancing their algorithms. The problem, nevertheless, is in gathering this information throughout varied platforms, as medical data is delicate and certain by strict privateness laws. For robots to succeed in their full potential, we’ll want in depth collaboration throughout hospitals, universities, and industries to coach these intelligent machines.
As autonomous robots make their manner into the medical world, we’ll face more and more advanced questions on accountability when one thing goes mistaken. The surgeon is historically accountable for all facets of the affected person’s care, but when a robotic acts independently, it’s unclear whether or not liability would fall on the surgeon, the producer of the robotic {hardware}, or the builders of the software program. If a robotic’s misinterpretation of knowledge causes a surgical error, for instance, is the surgeon at fault for not intervening, or does the blame lie with the know-how suppliers? Clear pointers and laws shall be important to navigate these situations and be certain that affected person security stays the highest precedence. As these applied sciences turn out to be extra prevalent, it’s additionally vital that sufferers be absolutely knowledgeable about the usage of autonomous systems, together with the potential advantages and the related dangers.
A state of affairs during which sufferers are routinely greeted by a surgeon and an autonomous robotic assistant is now not a distant risk, because of the imaging and management applied sciences being developed in the present day. And when sufferers start to learn from these developments, autonomous robots within the working room received’t simply be a risk however a brand new customary in medication.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet