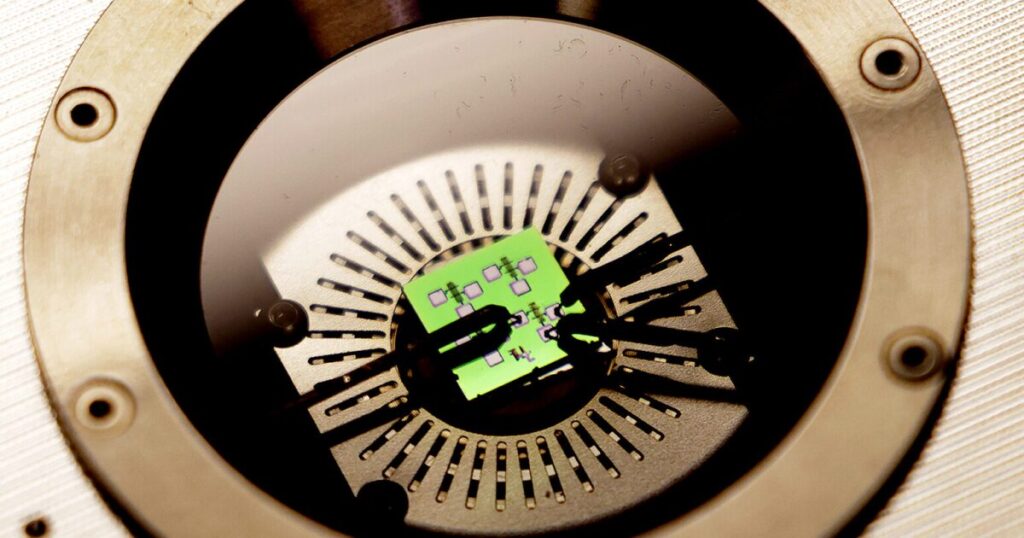
Computer systems usually go a bit wonky if you stick them within the oven for a bit, however engineers on the College of Michigan want to change that by growing a brand new laptop reminiscence that may run on the temperature of molten lead.
In the present day, computer systems are nearly all over the place, with the “nearly” shortly heading out the window. Solely 40 years in the past, having a pc (singular) in your automobile, for instance, was an actual dialog starter. In 2024, the typical automobile has about 100 computer systems unfold via its numerous methods working 100 million strains of code.
The issue is that as computer systems broaden their purposes, they’re ending up in environments which are very hostile to silicon microchips. These work tremendous at room temperature, however as they get hotter the way in which electrons circulation via the semiconductors begins to change. Once they attain 300 °F (150 °C), the circulation of electrical energy turns into uncontrollable and may start doing nasty issues like wiping the gadget’s reminiscence.
Brenda Ahearn/College of Michigan, School of Engineering, Communications and Advertising
That is unhealthy sufficient in our automobile instance the place chips are put in in hothouse spots just like the engine or brakes. Once they’re put into jet engines, foundries, fusion reactors, and Venus-bound house probes, the scenario turns into insupportable.
That is why the Michigan staff is engaged on a brand new laptop reminiscence that may retailer and rewrite info even when it is heated to over 1,100 °F (600 °C). It manages this by making a semiconductor out of layers of tantalum oxide and tantalum metallic with a strong electrolyte between them. As a substitute of transferring about electrons to retailer information, the reminiscence chip makes use of oxygen ions drawn via three platinum electrodes.
In accordance with the staff, the method is much less like a normal reminiscence and extra like how a battery works. In different phrases, it isn’t a lot digital as electrochemical. Shifting oxygen ions out of the tantalum oxide leaves a small spot of tantalum metallic. These adjustments make the layers act as both an insulator or a conductor, producing two voltage states that enable info to be saved as ones and zeros.

Brenda Ahearn/College of Michigan, School of Engineering, Communications and Advertising
Up to now so good. Sadly, the brand new reminiscence solely works at temperatures above 500 °F (250 °C), so a heater unit is required when it is in additional home settings. At present, it has been capable of maintain its reminiscence for twenty-four hours and in comparison with different high-temperature reminiscences it really works at decrease voltages. As well as, the staff sees it as having the potential of resulting in extra superior variations capable of maintain gigabytes of information.
“There’s a whole lot of curiosity in utilizing AI to enhance monitoring in these excessive settings, however they require beefy processor chips that run on a whole lot of energy, and a whole lot of these excessive settings even have strict energy budgets,” mentioned Alec Talin, a senior scientist within the Chemistry, Combustion and Supplies Science Division at Sandia Nationwide Laboratories. “In-memory computing chips may assist course of a few of that information earlier than it reaches the AI chips and cut back the gadget’s general energy use.”
The analysis was printed in Device.
Supply: University of Michigan