The simplification, studied intimately by a gaggle led by researchers at MIT, may make it simpler to know why neural networks produce sure outputs, assist confirm their selections, and even probe for bias. Preliminary proof additionally means that as KANs are made greater, their accuracy will increase sooner than networks constructed of conventional neurons.
“It is fascinating work,” says Andrew Wilson, who research the foundations of machine studying at New York College. “It is good that persons are making an attempt to essentially rethink the design of those [networks].”
The fundamental parts of KANs had been really proposed within the Nineteen Nineties, and researchers stored constructing easy variations of such networks. However the MIT-led workforce has taken the concept additional, exhibiting how you can construct and practice greater KANs, performing empirical checks on them, and analyzing some KANs to exhibit how their problem-solving capability might be interpreted by people. “We revitalized this concept,” mentioned workforce member Ziming Liu, a PhD pupil in Max Tegmark’s lab at MIT. “And, hopefully, with the interpretability… we [may] not [have to] assume neural networks are black bins.”
Whereas it is nonetheless early days, the workforce’s work on KANs is attracting consideration. GitHub pages have sprung up that present how you can use KANs for myriad functions, akin to picture recognition and fixing fluid dynamics issues.
Discovering the system
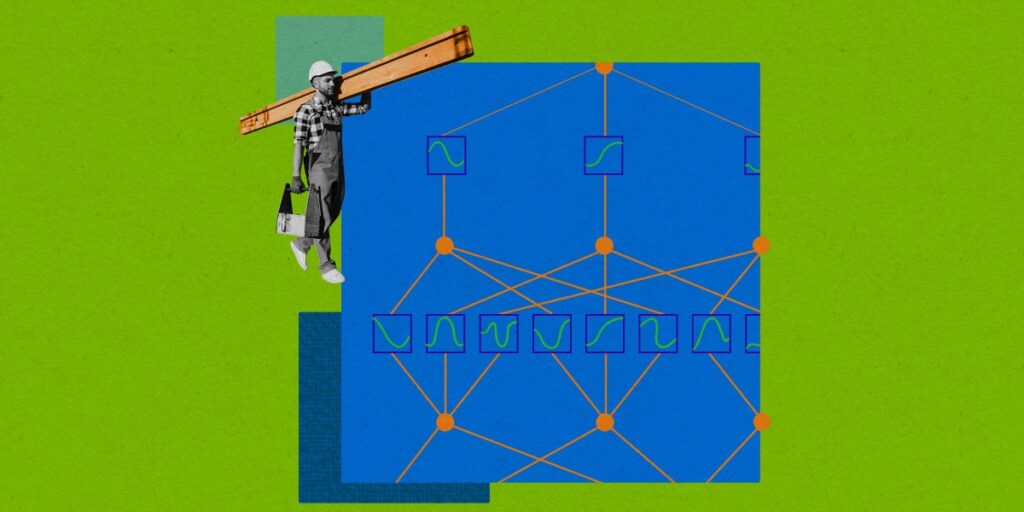
The present advance got here when Liu and colleagues at MIT, Caltech, and different institutes had been making an attempt to know the inside workings of normal synthetic neural networks.
Immediately, nearly all kinds of AI, together with these used to construct giant language fashions and picture recognition methods, embrace sub-networks generally known as a multilayer perceptron (MLP). In an MLP, synthetic neurons are organized in dense, interconnected “layers.” Every neuron has inside it one thing referred to as an “activation perform”—a mathematical operation that takes in a bunch of inputs and transforms them in some pre-specified method into an output.